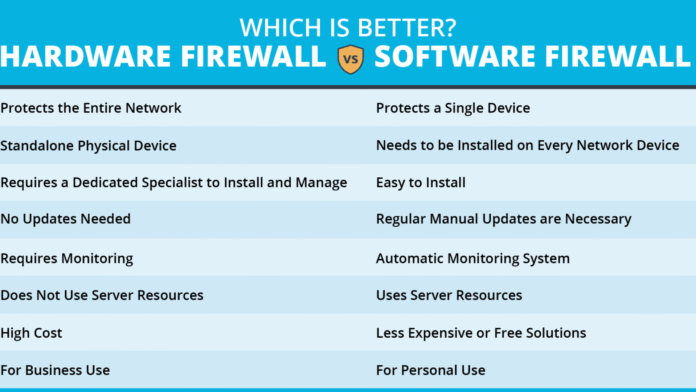
Firewalls are the network security front-line troops. These filters block any malicious requests and protect sensitive data. However, businesses have to make the choice between hardware firewalls versus software firewalls; each has its own set of benefits, configurations, and uses. Knowing these differences helps you make an informed decision.
1. What is a Hardware Firewall?
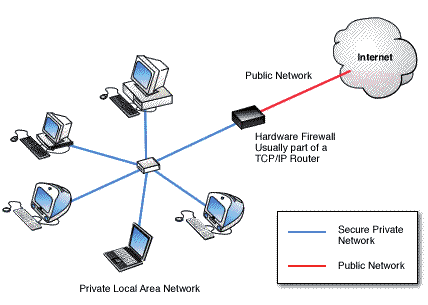
As a hardware firewall, we do consider the physical device placed between your company network and the Internet. Hardware firewalls analyze all incoming and outgoing network traffic before reaching any connected device. It works independently of computers, thus cutting down system performance overhead. In this aspect, it is very much useful in maintaining strong perimeter security for entire networks.
2. What Is Software Firewall?
Installing a software firewall on individual machines like laptops, desktops, or servers is another option. A software firewall controls application-layer traffic and detects any suspicious activity. It also allows very granular access rules, which makes it ideal for personal devices, remote workers, and small-scale setups.
3. Hardware vs. Software Firewalls: Major Differences
While hardware-based firewalls shield an entire network from one point, software firewalls put security around each device instead. Hardware solutions need dedicated equipment, while software runs on the systems already in place. Scale, budget, and security needs are what will ultimately define your choice.
4. Setting Up Hardware Firewalls
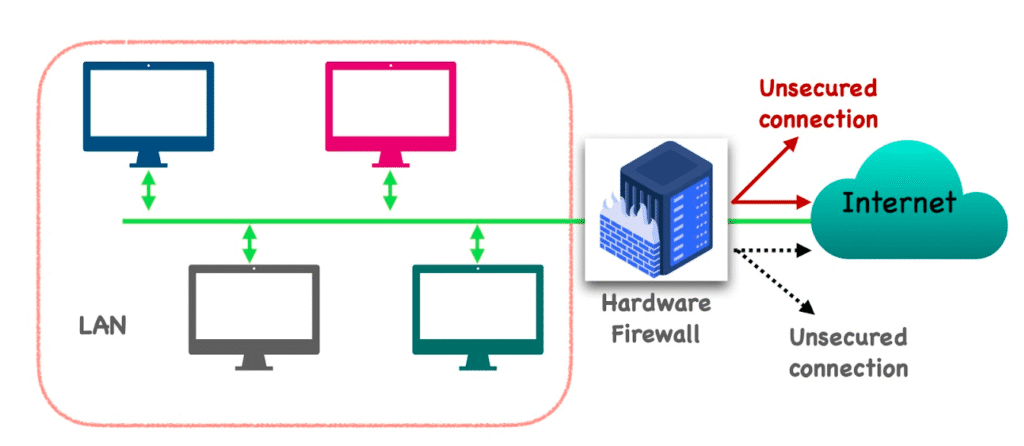
To set up a hardware firewall, install between your modem and router. Configure the rules via its web interface. Also, set the port forwarding, VPN access, or IP filtering. This will give you centralized control of all network devices.
5. Setting Up Software Firewalls
The software firewall installation is simple. Download, install, and configure the security settings. Enable automatic updates to keep protection up to date. Thus, every device will have a customized security profile.
6. Hardware Firewall Application
The hardware firewall is best for the business network, data center, and corporate environment. Moreover, it needs to be very effective in its handling of extremely high traffic volumes, securing DDoS protection, and securing all the connected devices from any possible external attacks.
7. Software Firewall Use Cases

Ideal for protecting remote workers, personal notebooks, and BYOD environments. Monitors application activity, blocks unsafe programs, and safeguards from internal threats. It thus supplements the protection hardware firewalls provide in their layered security models.
8. Hardware Firewall + Software Firewall
Most companies use hardware firewalls and host-based firewalls together. By perimeter protection, it has individual device protection. It lowers the possible vulnerabilities, covers a bigger threat portion, and provides multi-layered security.
Final Thoughts
Almost all systems whether software and hardware have their firewall under individual defense. The type to be used will then be determined by the specific size of the local network, the kind of data it has and the security measures required from this defense tool. By understanding the differences in these firewalls setup, functions, and specific uses, one can install a better defense against cyber threats.