Defense strategy is increasingly sophisticated in a world where cybercrimes are also on the rise. Businesses, regardless of their size, are daily targeted for data breaches, malware, ransomware, and other malicious activities. It then becomes obvious that the vault in which the information can be safely stored is a properly configured firewall. Though it is important to install the firewall in the first place, one must ensure that it is properly configured for maximum protection. This article will guide you through the best firewall settings to shield your business network effectively.
1. Defining and Segmenting Network Zones
A good network segmentation strategy could reduce the risk of breaches by a large margin. Ensure firewalls are configured to create distinct network zones within your business infrastructure. For instance, make different segments for:
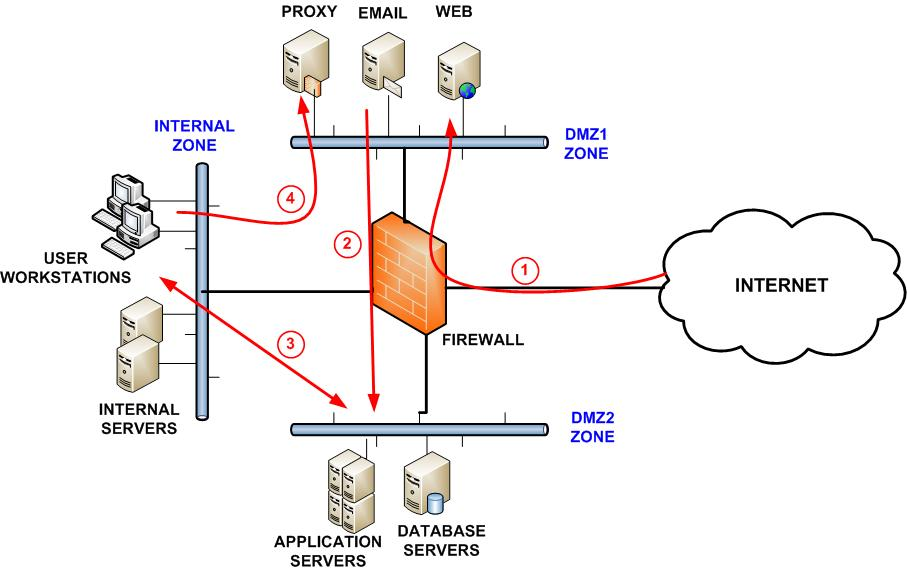
- Internal Systems (e.g., Employee workstations)
- Servers (e.g., Database servers, file servers)
- Guest Network (e.g., Public Wi-Fi)
- DMZ (Demilitarized Zone) for web servers or applications
Through this type of segmenting, security controls can be made to be far stricter, preventing access to the most sensitive portions of the network. Should there be an open breach, it makes it more complicated for an attacker to move laterally around your network.
2. Utilize Stateful Inspection and Deep Packet Inspection (DPI)
Stateful inspection checks the newer and older versions of the packet data according to some pre-set rules and context, thus detecting any probable malicious activity based on the packet’s pre-set connected state. Deep Packet Inspection (DPI) takes it a step further by analyzing its content, not just the header, which can identify more advanced attacks, such as exfiltration attempts and malware.
These two inspection methods offer more intelligence to your firewall and extend more scrutiny of both inbound and outbound traffic that can apparently lead to improved threat detection and blockage.
3. Impose Stringent ACL Policies
For instance, ACLs are like gatekeepers, responsible for imposing regulations in controlling access to network resources and what may be done once connected. Thus, ACLs do the job of allowing or disallowing sources for accessing the network. This means that users and devices must clearly and definitively discharge themselves and follow ACL regulations.
- Controlling both inbound and outbound traffic: Policy should restrain the communication of the affected service to that of any specified IP addresses or assigned exclusive subnets.
- Least Privilege: This will ensure that users and systems have the minimum level of rights required to carry out their jobs, reducing exposure to threats.
- Avoid generic rules, and always try to be specific: Do not adopt broad and permissive “allow” rules but rather conform to the principle of least privilege.
4. Keep Firewall Software Updated and Patched
To run, firewall software relies on Firewalls, another avenue through which an attacker can compromise the network and steal critical data. Thus, the need for the latest and well-configured firmware and software to ensure the security level of any commercial enterprise.

- Automated updates: increase the security level of most modern firewalls, either by enabling them to monitor updates and install them automatically when needed.
- Watch for release notes: Keep watch for vendor release notes and security advisories that might contain information on vital updates or exposures.
5. Deployment of the IDPS
An IDPS will complement the firewall by inspecting incoming traffic for suspicious patterns. Upon detecting anything that might cause trouble, it can instantly stop and block malicious traffic, thus adding an extra layer of defense.
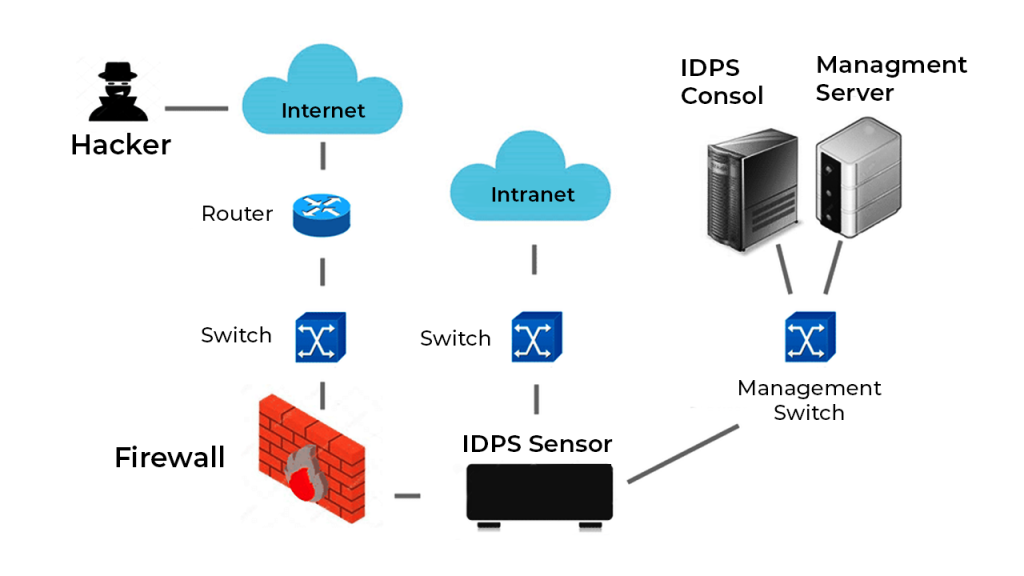
Configure your firewall allowing for both the detection and prevention features, ensuring that both inbound and outbound traffic are being monitored and filtered for known attack signatures or abnormal behavior.
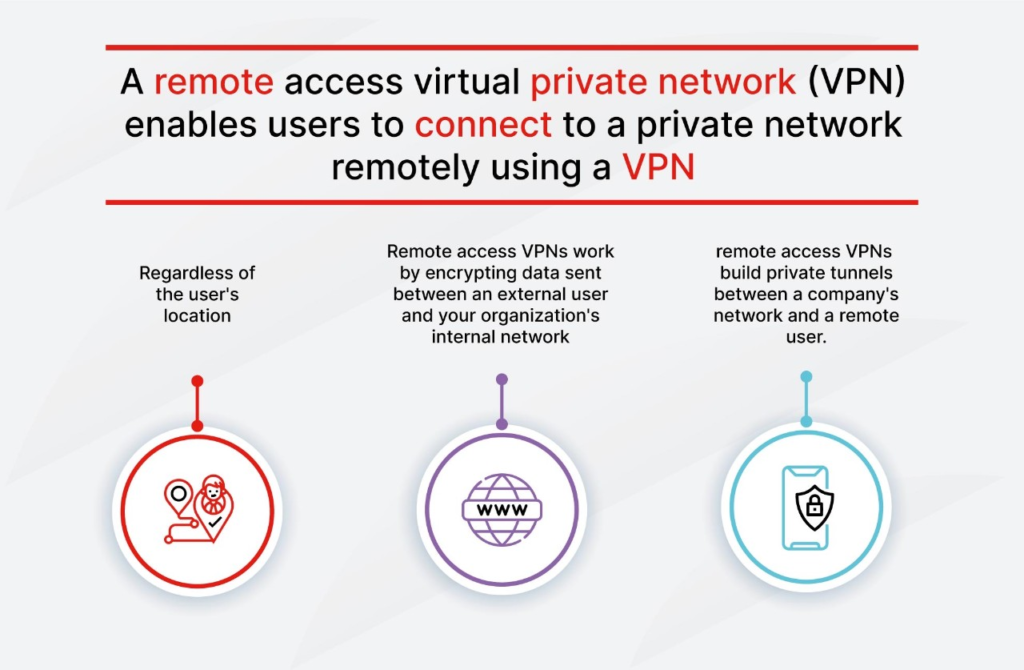
6. Virtual Network for Remote Access
In this period of remote work, Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) play a vital role in safe business network remote access. Instead of permitting staff to connect directly to your network through the internet, make sure your firewall mandates the use of VPN, encrypting data and verifying user credentials.
- Do not split-tunnel: To allow all network traffic to pass through a secure VPN, put an end to split tunneling so that traffic passes through the firewall.
- Secure authentication: Multi-factor authentication (MFA) enhances the security of VPN access.
7. Monitor Logs and Set Alerts
Firewall logs contain critical information that can point out potential security incidents. Regularly looking through the firewall logs helps spot suspicious behavior patterns, unauthorized access attempts, and so on.
- Automated alerts: Configure your firewall to issue alerts on potential malicious activities or violations. This will help secure your notifications for accurate real-time responses to potential threats.
- Comprehensive logging: For more significant organizations, throwing in a Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) system may help in collecting and analyzing log data across all these security devices, including firewalls.
8. Create Outbound Traffic Filters
Most organizations majorly regulate inbound traffic neglecting the broader perspective of outbound traffic. Compromised internal devices or user accounts are capable of forwarding sensitive data beyond the network. Hence, outbound traffic filtering becomes very important.
- Monitor the movement of sensitive data: Implement rules that monitor and forbid certain types of sensitive data such as financial records or customer information from going beyond the network.
- Limit non-critical services: Limit traffic to non-critical services or websites to reduce the attack surface and flinch any unwanted data exfiltration.
9. Implement application-layer filtering
Many contemporary threats exploit vulnerabilities in specific applications such as web browsers, email servers, or file sharing protocols. Configuring firewalls to block applications-layer traffic to an extent is the most effective way to block such attacks by blocking traffic from or to the least secure applications.
- Web Filtering: At least inhibit or block access to malicious websites that usually host malware or phishing schemes.
- Email Filtering: Integrate email filtering rules that prevent phishing attempts, spam, and malicious attachments from entering your network.
10. Make use of DNS filtering
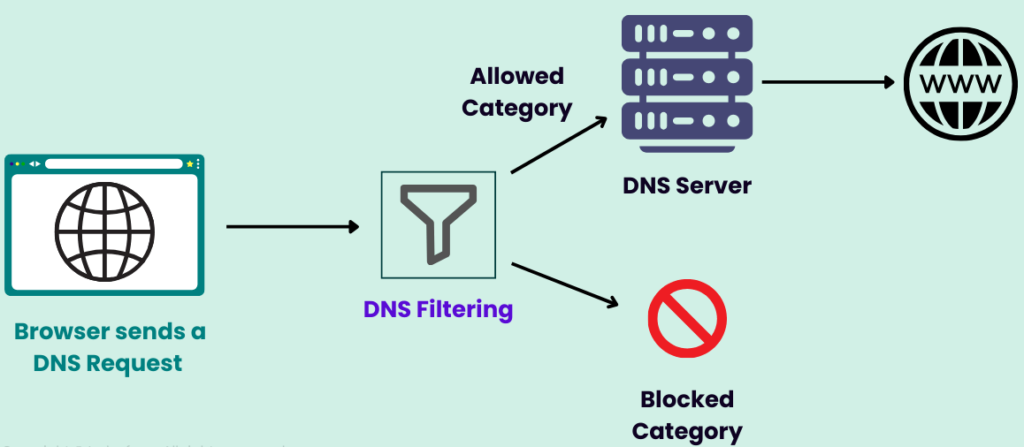
DNS filtering is a way to restrict users from visiting harmful websites by blocking domain names participating in-harmful activities. Setting up the DNS at the firewall level will lend an extra layer of protection against your employees trying to enter hazardous sites that possibly harbor ransomware, malware, or phishing attacks.
Conclusion
The firewall is the defense you put in place for your network to confront all external threats. It is an important security tool, but its effectiveness depends critically on configuration and regular updates. Shaping network houses, deploying advanced inspection methods, finer segmentation of access, and the layering of additional security components IDS/IPS, VPN, and DNS filtering will guarantee the safety of your business network against these threats. Remember, network security equates to a continual work in progress and not one shot fixes. Reviewing firewall settings constantly and staying apprised of prevailing threats.
Should you need assistance configuring the firewall or reviewing the security settings, consult a network security professional to give you the highest degree of protection for the needs of your business.