VLANs are the basic building blocks of modern networking, allowing for the logical segmentation of a physical network for better security, performance, and management. For effective network management, it is indispensably important to comprehend the essential difference between Layer 2 VLANs and Layer 3 VLANs. Thus, the guide will take a closer look at L2 and L3 VLANs concerning their operation and application.
Understanding the Fundamentals of VLANs

Before jumping into things like L2 and L3 VLANs, let us review the basic idea of a VLAN. A VLAN is a means of separating a physical network into multiple logical networks or broadcast domains. Such segmentation can improve security by isolating traffic and, at the same time, improve the segment’s performance due to reduced broadcast traffic within it.
Layer 2 VLANs
The L2 VLAN stands for Layer 2 Virtual Local Area Network. This simple virtual network is based on the MAC address of hosts and allows switching-based network activities without worrying about the actual subnet of hosts connected to the network.
Broad Characteristics of L2 VLANs:
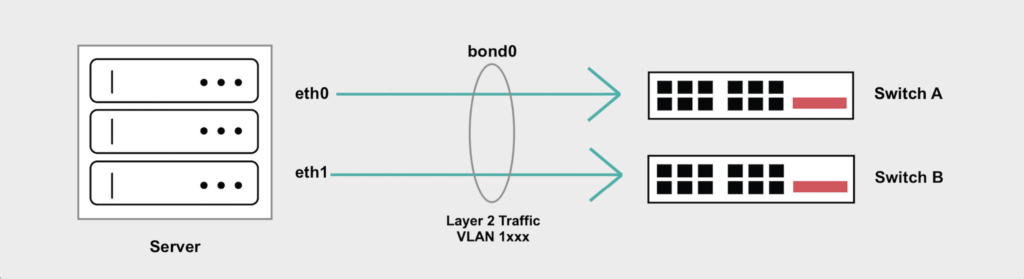
- MAC Address-Based: Traffic forwarding in L2 VLANs follows MAC addresses, so devices are usually in the same subnet.
- Single Broadcast Domain: All devices in an L2 VLAN will broadcast their messages into the same broadcast domain.
- Switching Functionality: L2 VLANs are made to switch traffic daily based on MAC addresses and VLAN tags (802.1Q).
- Same Subnet: All devices in an L2 VLAN should have the same IP subnet.
- Intra-VLAN Communication: The communication occurring within an L2 VLAN is switching at Layer 2.
Uses of L2 VLANs
- Departmental Segmentation: Provides different VLANs for departments (such as HR, IT) to separate them for security and traffic purposes.
- Voice VLANs: To ensure that voice traffic is separated to enhance Quality of Services.
- Guest Network: An isolated guest network for visitors.
The third layer of VLANs relates to Layer 3
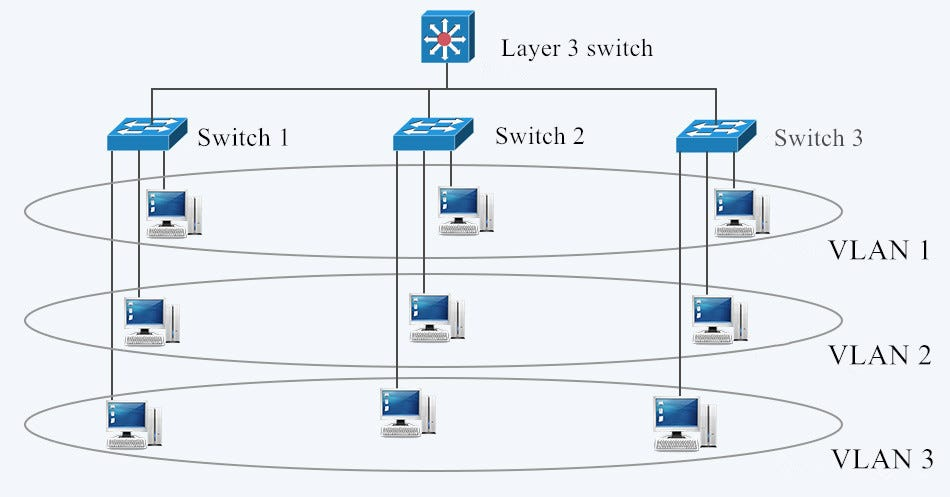
L3 VLANs-Layer 3 VLANs operate at Network Layer (Layer 3) of OSI model. It provides routing functions and thus enables different subnetworks to communicate with each other.
The Key Features of L3 VLANs:
- IP Address-Based: IP Address is being used for L3 VLANs to route traffic flows between different subnets.
- Inter-VLAN Routing: There will be no need anymore to make communication between different VLANs within the same.
- Router or L3 Switching: L3 VLANs will require a router or L3 switch for routing.
- Different Subnets: Devices attached to various L3 VLANs can belong to various IP subnets.
- Virtual Interfaces: L3 uses virtual interfaces such as Switch Virtual Interface or SVI to represent virtual local area networks on an L3 device.
Applications of L3 VLANs
- Inter-VLAN Routing: Communication among various VLANs.
- Network Segmentation with Routing: Network segmentation right from routing for effective traffic flow.
- VLAN Routing with Access Control Lists (ACLs): Using granular access control in inter-VLAN communications.
- Route Summarization: Minimizing size and complexity of the routing table.
L2 VLAN vs. L3 VLAN: Key Differences
| Feature | L2 VLAN | L3 VLAN |
| Layer of Operation | Data Link Layer (Layer 2) | Network Layer (Layer 3) |
| Addressing | MAC Addresses | IP Addresses |
| Functionality | Switching | Routing |
| Communication | Intra-VLAN (same subnet) | Inter-VLAN (different subnets) |
| Device Required | Switch | Router or L3 Switch |
| Broadcast Domain | Single | Multiple (with routing) Export to Sheets |
What’s the difference between choosing L2 or L3 VLAN?
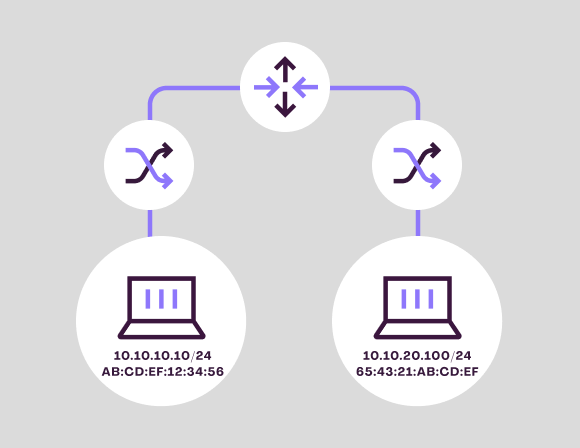
- L2 VLANs: Use when you want to segment a network on the same subnet.
- L3 VLANs: Use when you need to route traffic from one subnet to another or to route traffic from one VLAN to another.
Conclusion
Knowledge of the distinction between L2 and L3 VLANs is crucial for designing and managing networks. L2 VLANs permit segmentation within the same subnet, while L3 VLANs allow routing between different subnets. Thus administrators may use the appropriate VLAN type to improve performance, enhance security, and build scalable network architectures.




This guide made VLAN concepts so easy to understand! The clear breakdown of L2 vs L3 and practical examples really helped me apply it in my small business network setup.
I really appreciated how clearly you explained L2 and L3 VLANs. Networking topics can get overwhelming, but your step-by-step breakdown and practical examples made it easy to follow. This guide is a great resource for both beginners and IT pros!