In the age of digitization, speed is almost completely often king. We want things like even faster downloads, shorter loading times, and fluid streaming. Of course, bandwidth – that is to say, the amount of data that can be transferred across over a certain time – has its important role to play but just as important, if not more so, is actually the other important factor that influences tremendously our online experience: primary benefit of lower network latency.
Network Latency explains Round Trip Delay.
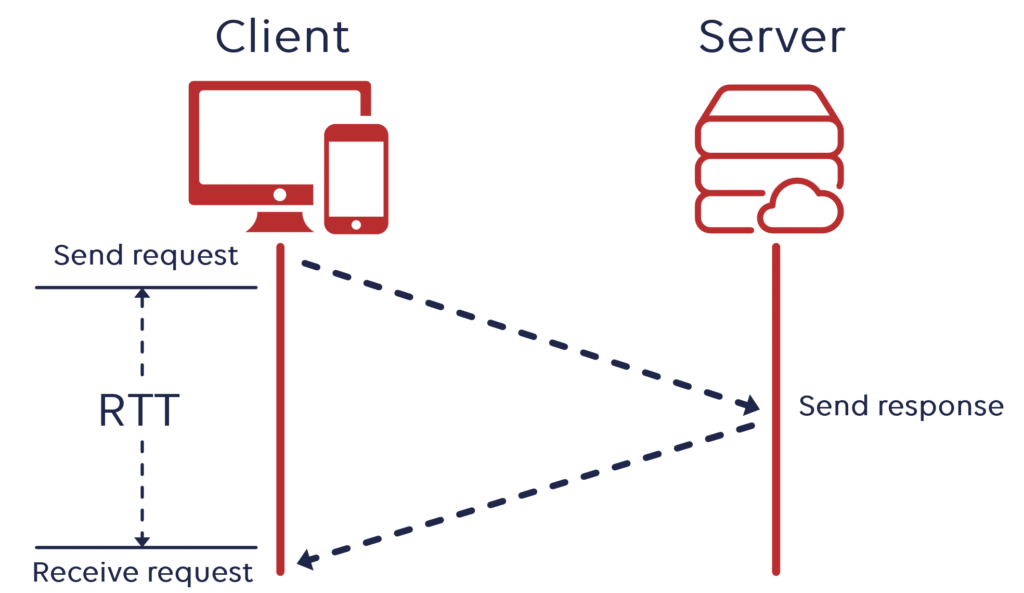
Latency is considered as length of time for any packet to travel from particular device to the server and back. To get round trip, certain factors affect latency: Physical distance cover, number of hops across the network, congestion along path. High latency means high delay-a feeling of slowness during online activity, which contributes to frustration.
The Primary Benefit: The Illusion of Immediacy
The longest of these benefits in this region is of low latency in the network, whereby it leads to the development of a state of immediacy and real-time interaction. When the latency low, the communication between one’s actions and response by server becomes indiscernible to naked eye and brain. Such seamless back-and-forth communication is a key parameter determining a great user experience in an application.
- Online Gaming: For gamers, low latency is important, often referred to as “Ping.” Milliseconds make the difference between winning and losing in very fast-paced multiplayer games. Because of low latency, the server registers your action immediately, leading to smooth movement and better, more accurate aiming without delay—ensuring an even playing field.
- Video Conferencing and VoIP: In virtual meetings and voice calls, low latency ensures smooth, natural conversations. Holdups may lead awkward pauses, overlapping speech, and breakdown of communication: Although, minimal latency, transmissions would allow real, face-to-face experience. Rendering near real-time audio-video communication during dissemination of distance working and virtual collaboration.
- Remote Desktop and Cloud Applications: Low latency tends to be crucial for a responsive experience accessed across an online computer or an application that should be cloud-based. Delays often create an atmosphere that makes people feel as if they’re working through molasses, in many cases, hence slow productivity.
- Financial Trading: The case high-frequency trading, it’s not long time interval before minimal delay may bring significant amounts money loss.
- Emerging Technologies: Indeed, as we progress towards more near real-time and interactive technologies such as the metaverse, advanced AR/VR experiences, or autonomous cars.
The Most Important Thing Beyond Speed: Responsiveness

Aiming for most of a meaningful experience through an internet connection is what the high bandwidth solicits a user to download large amounts of files almost immediate. He can have a very wide pipe, high bandwidth, but it does not guarantee low latency or delays. Imagine a very wide highway with a big traffic jam; so much communication moves theoretically but doesn’t reach its target in time.
Latency, on other hand, opens way for fast round-trip travel packets comprising data, thus making up the crucial sense of immediacy.
Above all, Factors That Affect Latency:
In knowing the benefits that low latency brings, one has-though at a basic level-to understand what affects low latency:
- Distance:The important consideration is the physical distance data travels; the farther the server, the higher the latency will likely be.
- Network Hops: Each router and every network device the data traverses adds a little latency.
- Congestion: This is very like a traffic jam in the streets where the aforementioned could substantially increase latency.
- Transmission Medium: Generally speaking, fiber optics will provide lower latency than copper wire.
- Server Response Time: The server to process a request and generate a reply is also a contributor to the total latency.
Final Word: Making Access Priority for Enhanced Digital Future
The lower latency networks contribute comprehensive bandwidth, which is primarily beneficial in providing a very responsive and real-time online experience. This ingredient makes information flow for seamless gaming, natural communication, realistic remote work, and is the foundation for future interactive technologies. As our digital lives demand increasingly instant communication, lower latency networks will likely lay the groundwork for a future that fully realizes the internet’s potential.



Great breakdown of how low latency enhances real-time experiences—especially in areas like gaming and video calls where milliseconds really matter. I’d love to see more discussion around how this plays into emerging tech like remote robotics or AR/VR, where latency can make or break the user experience.
Great breakdown of how latency affects real-time online experiences. People often confuse bandwidth with latency, but as you point out, lower latency can make a bigger difference in activities like gaming and video calls.
Great breakdown of why low latency matters—especially for thingsBlog Comment Creation Guide like gaming and video calls where even slight delays can really disrupt the experience. One angle that might be worth exploring in a follow-up is how edge computing plays a role in reducing latency, especially as IoT devices become more widespread.
This is a great breakdown of why low latency matters so much—especially in real-time applications like online gaming and video calls where even a slight delay can throw off the entire experience. It might also be worth touching on how lower latency benefits emerging tech like autonomous vehicles and remote surgeries, where precision and timing are everything.